Supervised Learning: The Foundation of Predictive Modeling
Editor’s note: This article is a part of our series on visualizing the foundations of machine learning. Source link
Editor’s note: This article is a part of our series on visualizing the foundations of machine learning. Source link
Large language models like LLaMA, Mistral, and Qwen have billions of parameters that demand a lot of memory and compute power. Source link
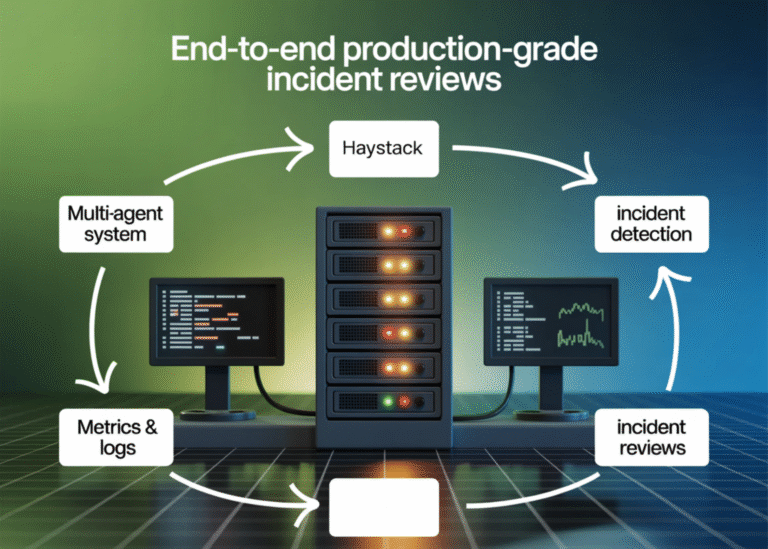
@tool def sql_investigate(query: str) -> dict: try: df = con.execute(query).df() head = df.head(30) return { “rows”: int(len(df)), “columns”: list(df.columns), “preview”: head.to_dict(orient=”records”) } except Exception as e: return {“error”: str(e)} @tool def log_pattern_scan(window_start_iso: str, window_end_iso: str, top_k: int = 8) ->…
Most forecasting work involves building custom models for each dataset — fit an ARIMA here, tune an LSTM there, wrestle with <a href=" Source link
Finishing Andrew Ng’s machine learning course <a href=" Source link

For decades, predicting the weather has been the exclusive domain of massive government supercomputers running complex physics-based equations. NVIDIA has shattered that barrier with the release of the Earth-2 family of open models and tools for AI weather and climate…
Clawdbot is an open source personal AI assistant that you run on your own hardware. It connects large language models from providers such as Anthropic and OpenAI to real tools such as messaging apps, files, shell, browser and smart home…
We initiate this tutorial by configuring a high-performance evaluation environment, specifically focused on integrating the DeepEval framework to bring unit-testing rigor to our LLM applications. By bridging the gap between raw retrieval and final generation, we implement a system that…

StepFun has introduced Step-DeepResearch, a 32B parameter end to end deep research agent that aims to turn web search into actual research workflows with long horizon reasoning, tool use and structured reporting. The model is built on Qwen2.5 32B-Base and…
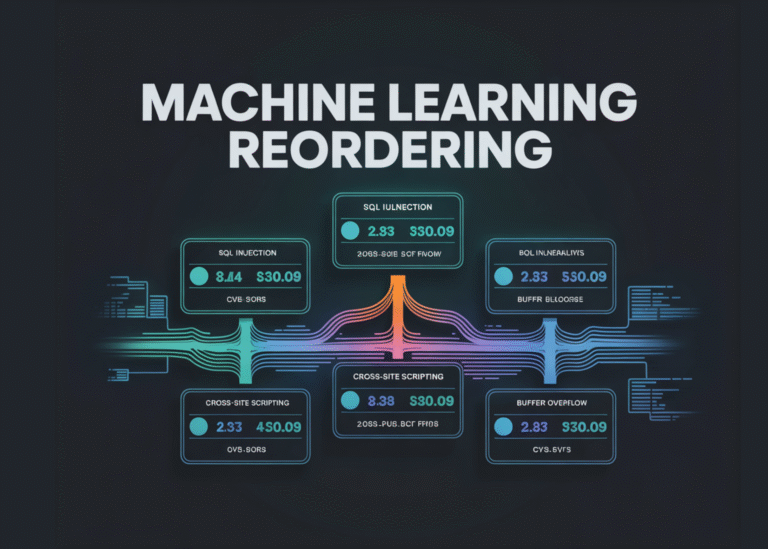
def visualize_results(df, priority_scores, feature_importance): fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(18, 10)) fig.suptitle(‘Vulnerability Scanner – ML Analysis Dashboard’, fontsize=16, fontweight=”bold”) axes[0, 0].hist(priority_scores, bins=30, color=”crimson”, alpha=0.7, edgecolor=”black”) axes[0, 0].set_xlabel(‘Priority Score’) axes[0, 0].set_ylabel(‘Frequency’) axes[0, 0].set_title(‘Priority Score Distribution’) axes[0, 0].axvline(np.percentile(priority_scores, 75), color=”orange”, linestyle=”–“, label=”75th…