The MIT-Portugal Program enters Phase 4 | MIT News
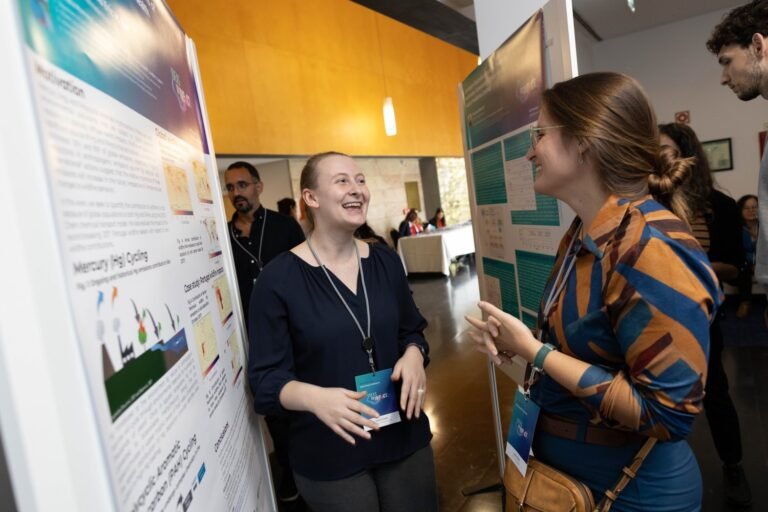

Since its founding 19 years ago as a pioneering collaboration with Portuguese universities, research institutions and corporations, the MIT-Portugal Program (MPP) has achieved a slew of successes — from enabling 47 entrepreneurial spinoffs and funding over 220 joint projects between…